civet


civet pipeline
Detailed description of the civet analysis pipeline
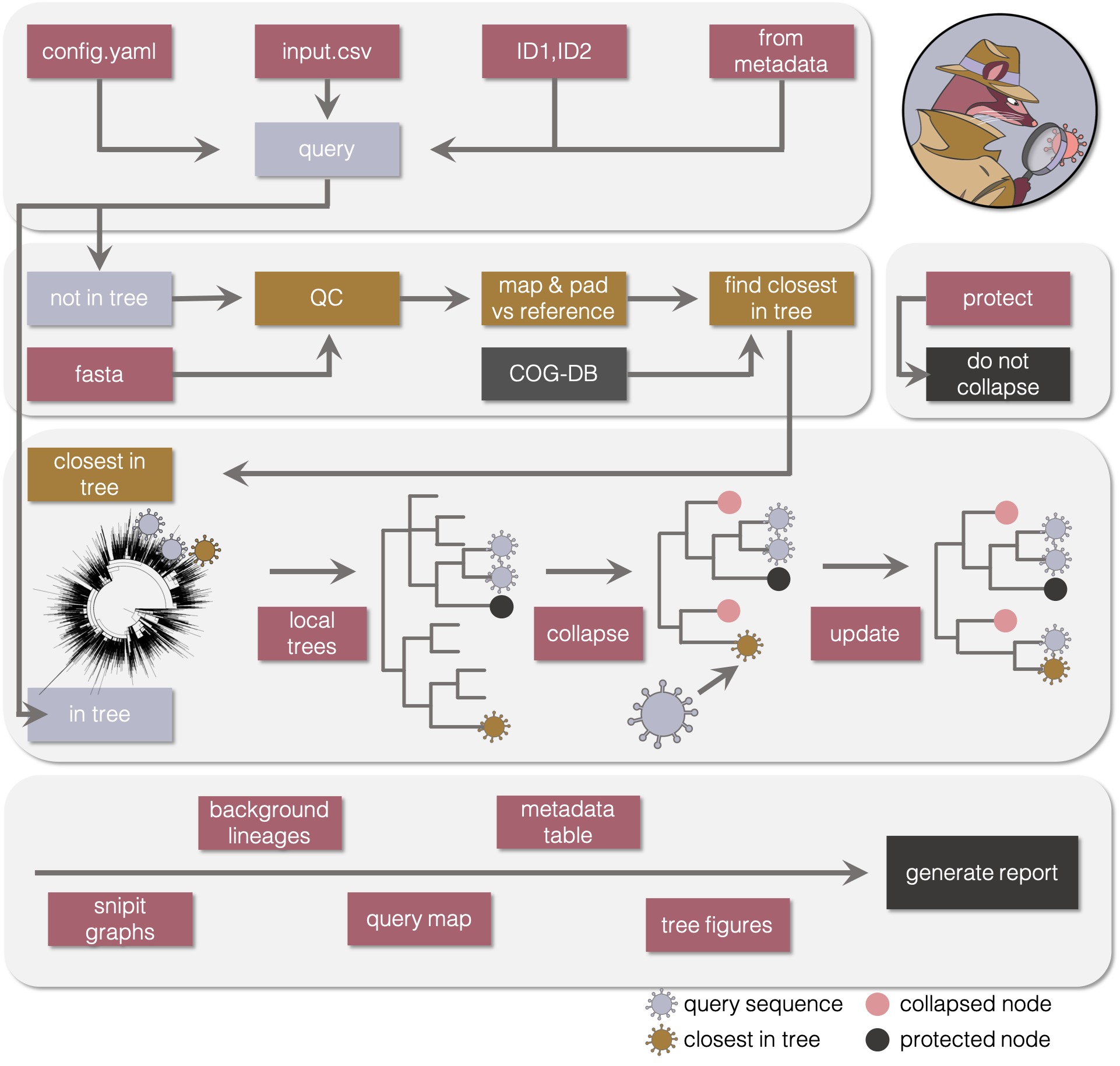
Initialising directories & detect input type
- Detect the input type (
-i / --input), either csv, yaml/yml or a string of IDS (or else a-fmsearch pattern). - If a string of IDs, they’re written to a temporary ‘input.csv’ file
- Loads default values
- If a yaml file is detected, all options specified are loaded and overwrite defaults
- Any command line arguments then overwrite the options specified in config file
- Output directory: if given, get path and create directory if necessary
- Set up temporary directory, can be configured but by default is $TEMPDIR. If
--no-temp, set temporary directory to the output directory
Finding COG-UK data
- If
--CLIMB, check path to civet directory exists, which verifies the user is on CLIMB - If
--datadiris specified and the--remoteflag is not used, check if it has the appropriate files - If
--datadirnot given, default to look for a directory called ‘civet-cat’ in the current working directory - If
--remotehas been specified, rsync data from CLIMB If rsync fails exit with informative error - If SSH keys not configured, specify
--remotealongside-uun - Check background metadata has
data_column(default: central_sample_id)
-fm / –from-metadata
- Exit if used in conjunction with input.csv, ID string or fasta options (not compatible yet)
- Find all records in the background metadata that match search criteria and pass on into civet as queries
–protect
- Find all records in the background metadata that match search criteria and pass on into civet to not collapse
QC on input csv
- Check the file exists
- Check the file has
input_column(default: name)
QC on input fasta
- If specified, check if input fasta file exists, otherwise exit with informative message
- Check
--min-length(Default: 10,000) - Check
--max-ambiguitycontent (Default: 0.5) - Check if sequence name in the input.csv file
- Write out failed query ids and why they failed (to pass to report)
- Write out sequences that passed QC to pass into pipeline
- If no sequences pass (or no fasta is given), check if any queries in the input.csv match with the database (if not, exit)
Access installed package data
- Find reference fasta file for downstream datafunk command
- Find polytomies figure for the report
- Find the report template
- Find map files
- If
-sc / --sequencing-centrespecified, check it’s a valid centre name and find the appropriate header for the report. If not a real sequencing centre, exit and display valid names
QC of mapping and report configuration
- Load the report options
- Check if the columns specified exist in the metadata
Configure local tree size and collapsing
- Check
--up-distanceand--down-distance, if either are not specified, use--distance(default: 2) - Check if the columns specified exist in the metadata
- Add
--collapse-thresholdinput
Load the free text specified for the report
- Make the report title
- Parse free text specified in the config file
Miscellaneous arguments
- Any option not specified as a cmd line argument or in a config file defaults to default values
- If
--verbose, print shell commands set to True, quiet mode off and custom logger disabled - If
--launch-browser, launch grip at end of report generation --threadsadded for number of parallel jobs to run- If
--generate-config, dump these config options to a file and exit
Pass options to snakemake
Passing through the configuration dictionary and setting the working directory to the temporary directory (if --no-temp, this inherits the output directory).
check_cog_db
Check against the COG-UK phylogenetics database for your query id, will check search field, which by default is central_sample_id, this finds all sequences that will already be in the big tree. Use data_column to configure a custom search field.
get_closest_cog
If you have supplied an additional fasta file with sequences that haven’t yet been uploaded to the COG-UK database, this side pipeline finds the closest matching sequence. This workflow returns a csv of the closest hits within the background phylogeny for each query not already in the tree. This information gets added to the report. It also returns the input query sequences aligned, with the UTRs masked out.
1) non_cog_minimap2_to_reference
Map the query fasta file containing sequences from CLIMB that didn’t meet the phylogenetic cut offs and sequences from the input fasta file against the Wuhan-Hu-1 reference sequence (Genbank ID: MN908947.3). This mapping runs minimap2 with the present option asm5 that is configured for mapping a long, closely related assembly against a reference.
2) non_cog_remove_insertions_and_trim_and_pad
This step runs the datafunk command sam_2_fasta, which parses the cigar strings produced by minimap2 and scaffolds the query sequence against the reference by removing insertions relative to the reference. The insertions are logged in a text file for reference, and can be retrieved by running civet with the --no-temp flag. This step also masks the UTR regions with N’s as the terminal ends of the genome.
3) gofasta
The padded, mapped set of query sequences then get compared against all COG-UK and all GISAID, and finds the top hit within the database for each query.
4) parse_closest
The output is parsed and the relevant COG-UK metadata and fasta sequences are pulled out of the big database.
combine_metadata
Metadata from the closest COG sequence is combined with the metadata found directly within the database.
prune_out_catchments
Using the names of the closest COG sequences and of the sequences already in the tree, jclusterfunk pulls out local trees with a radius of --distance number of nodes are pulled out of the large global tree. Optionally, --up-distance and --down-distance can be used to pull out more parent or more child nodes.
process_catchments
Another sub-workflow that gets spawned off with the set of catchment trees produced from the prune_out_catchments rule. In brief there are two alternative snakefiles can can be called at this step depending on whether new sequences need to be added into the tree or not. The output of this step is a directory of “local_trees” that have the nodes we have not queried collapsed to the nearest polytomy, with an output summary file of the tips that had been in that sub-tree prior to collapse.
Either run: 1) just_collapse_trees.smk if no new sequences need to be added to the phylogeny. or 2) process_collapsed_trees.smk if new trees need to be estimated with query sequences added in.
just_collapse_trees.smk
1) summarise_polytomies
clusterfunk focus is run, which collapses and summarises non-query or non-closest sequences to the parent polytomy and outputs a summary file of the tips that make up the collapsed node.
2) remove_str_for_baltic Processes the tip names to make them readable for the baltic tree parser.
3) to_nexus Converts each tree from newick to nexus format.
4) summarise_processing Combines all the information about collapsed tips into a single file.
process_collapsed_trees.smk
1) get_basal_representative For each catchment tree, identify basal tip that can be used as to represent a subtree during the iqtree tree building step
2) get_basal_seq Extract the basal sequences from the background_seqs file
3) combine_basal Combine these sequences into a single file
4) protect_subtree_nodes
Define the set of nodes that will need to be protected from collapse.
These include
- Any tip matching the name of a local tree
- Any tip that matched the criteria given with --protect
- Any query that matched the criteria given with --from-metadata
- Any query sequence given in the input.csv query file or given as an ID string
5) summarise_polytomies
clusterfunk focus is run, which collapses and summarises non-query or non-closest sequences to the parent polytomy and outputs a summary file of the tips that make up the collapsed node.
6) get_collapsed_representative For each collapsed node, the sequences of the tips that comprise that collapsed node are pulled out of the global alignment and a basal sequence is selected to represent that node in the phylogeny.
7) extract_taxa All taxon labels are extracted from the collapsed phylogeny.
8) gather_fasta_seqs Each tip in the tree gets matched either to its own sequence or a representative sequence (if a collapsed node). An outgroup sequence is also added to the set of sequences. Any sequences from the input fasta file for that tree are also added to the alignment.
9) hash_for_iqtree
A hash for taxon labels is created for the input to iqtree so it doesn’t corrupt the sequence names.
10) hash_tax_labels
clusterfunk relabel_tips is run that relabels the tips of the tree with the taxon hash.
11) iqtree_catchment
iqtree is run on the new alignment with added sequences, with -m HKY and -au options.
12) restore_tip_names
The hashed tip names are restored with the same clusterfunk relabel_tips command.
13) prune_outgroup outgroup sequence is removed from the tree, whose root was scaffolded by the outgroup
14) remove_str_for_baltic Processes the tip names to make them readable for the baltic tree parser.
15) to_nexus Converts each tree from newick to nexus format.
16) summarise_processing Combines all the information about collapsed tips into a single file.
find_snps
A side pipeline that runs snipit on your set of query sequences, producing a figure that summarises all the snps relative to the reference sequence. Turn these figures off with --no-snipit. These figures also automatically don’t get generated if -fm / --from-metadata is specified.
regional_mapping
A side pipeline that will render maps summarising the variation in the local area surrounding your query sequences of interest.
regional_map_rendering
Render the figures showing local maps
make_report
Parses metadata CSVs and any input csv provided, along with tree files generated previously. There are a number of different options for figures, some of which must be specified when calling CIVET.
The report broadly consists of:
- A list of those sequences which did not meet quality control requirements
- Two summary tables containing information about sequences which were already in the database, and those which were not, but had sequence data provided in fasta file.
- Trees showing the phylogenetic context of each of the query sequences which passed quality control.
There also a number of optional figures, including different SNP data tables, maps and bar charts describing collpased nodes.
For information on these optional figures and how to configure the core report, see the report documentation and map documentation files.
launch_grip
Converts md to an html file and optionally launches the report in a browser window with --launch-browser